

If you are new to Git follow the 15 min TryGit Tutorial to get a quick introduction to Git.Ģ.
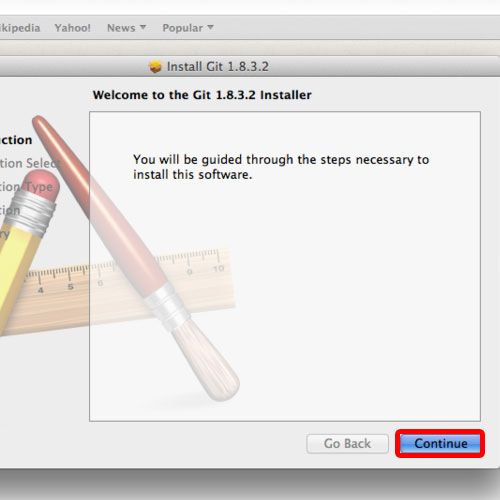
Additionally you will also need a GitHub account. Installation: To get started you need the following software installed on your computer: Git and if you are new to R, then you also need to install R and RStudio. RStudio integrates support for git, hence we are going to use the widely used combination R + Git + RStudio. GitHub is a user-friendly webservice that allows you to store your project repository remotely. install.packages("devtools") devtools::install_github("username/packagename") (Development of R packages is more advanced in R, but is a well-structured way to keep your projects tidy see: R Packages by Hadley Wickham) And you can install development packages of others with two lines of code.
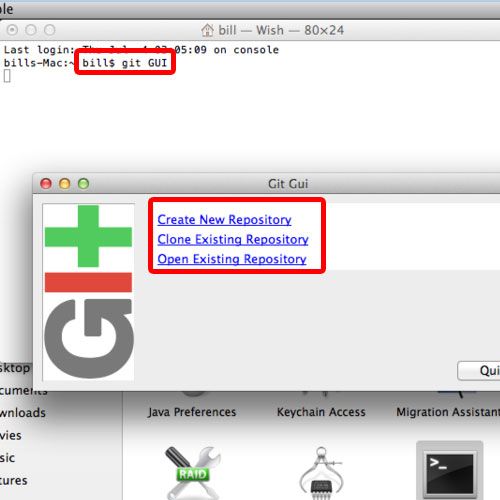
You can revert back to a previous version, if you find errors or accidently deleted something.You can also report errors (bugs) or suggest new additions (features) to projects. People can contribute to your project and vice-versa. It makes sharing of your projects easy (once it’s setup, you’ll get there).Git allows you to track and share your code and analysis. R in combination with the distributed version control system Git provides a convenient setup to make your research project reproducible. Clone/fork an existing project from GitHub.(The tutorial was originally created on GitHub and hosted here.) This tutorial in the context of the Reproducible Research Workshop provides you with the first steps on how to use Git with R and RStudio.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
